 Editing Textures
Editing Textures
 Editing Textures
Editing TexturesA texture is an image or sequence that is imported onto a material. A material can receive one or more textures.
 Add Texture button in the Shaders inspector
Add Texture button in the Shaders inspector and selecting the Add Texture... option
and selecting the Add Texture... option button to delete the current texture.
button to delete the current texture.

Displays the thumbnail of the selected Texture. The blue cross represents the anchoring point of the texture. Clicking in the image repositions this point.
Use the circular cursor (Shift + Click, to step every 15°) to turn the texture on its axis or enter a value in the related field.
Check and click on the selector to choose a color.
Move the slider to change the reflection or enter a value in the related field. When the diode is red, the texture reflects its environment.
Double click on the red diode to cancel the effect.
Entering a Limit value defines the maximum distance of the reflection.

Use the slider or enter a value into the related field.
Use the slider or enter a value into the related field.
Use the slider or enter a value into the related field to simulate the effect of bumps or hollows on the surface of the material using the levels of gray contained in the image.
Double click on the diode to cancel the effect.
Normal mapping
Apply a level of transparency to the texture or enter a value into the related field. Click on the diode to cancel the effect.
Use Alpha Channel: Activates/deactivates the transparency of the alpha channel.
Using a transparency color: Click on the selector to choose a transparency color.
Button
 : The texture is automatically adjusted to cover the maximum surface of the material horizontally and/or vertically.
: The texture is automatically adjusted to cover the maximum surface of the material horizontally and/or vertically.
The slider changes the texture scale from 50 to 200% of the current size. Or enter a value into the related field.
Width/Height:

Enter the size of the texture, clicking on ![]() retains the proportions. Click again to cancel the limitation.
retains the proportions. Click again to cancel the limitation.
Horizontal/Vertical Spacing:
Used for repeated textures. Defines the size of the spacing between each repetition.
Enter a spacing value as H and/or V. Clicking ![]() keeps the same proportions. Click again to cancel the limitation.
keeps the same proportions. Click again to cancel the limitation.
Flip:  horizontally or vertically inverts the texture with a mirror option between 2 repetitions.
horizontally or vertically inverts the texture with a mirror option between 2 repetitions.
Horizontal, Vertical repetition: duplicates the texture along the horizontal and/or vertical axis.
Horizontal Mirror, Vertical Mirror: Horizontally and/or vertically inverts each duplication.
Adjusts the image to the surface on which it is placed. Automatically selects the adjustment best suited to the project.
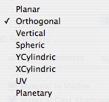
Planar: is applied to a plane.
Orthogonal: is applied to an element. If the element is composed of surface planes, the texture follows the surface planes.
Vertical: vertical projection on the element. The horizontal parts receive the image while the vertical or tilted parts are stretched.
Spherical: adopts a spherical form that depends on the size of the texture. Hence, it may leave empty spaces.
YCylindric: the texture is projected around the axis of a vertical cylinder.
XCylindric: the texture is projected around the axis of a horizontal cylinder.
UV: maintains the texture coordinates on an object coming from software that manages UV maps.
Planetary: vertical projection of the element while passing through the poles, without leaving spaces.
For a material, this makes it possible to navigate between related Shader and Textures editors.
|
Artlantis User Guide: Editing Textures |
|
© 2009 Abvent www.artlantis.com |